Bull Terrier as a Therapy Dog
Get Your Documents
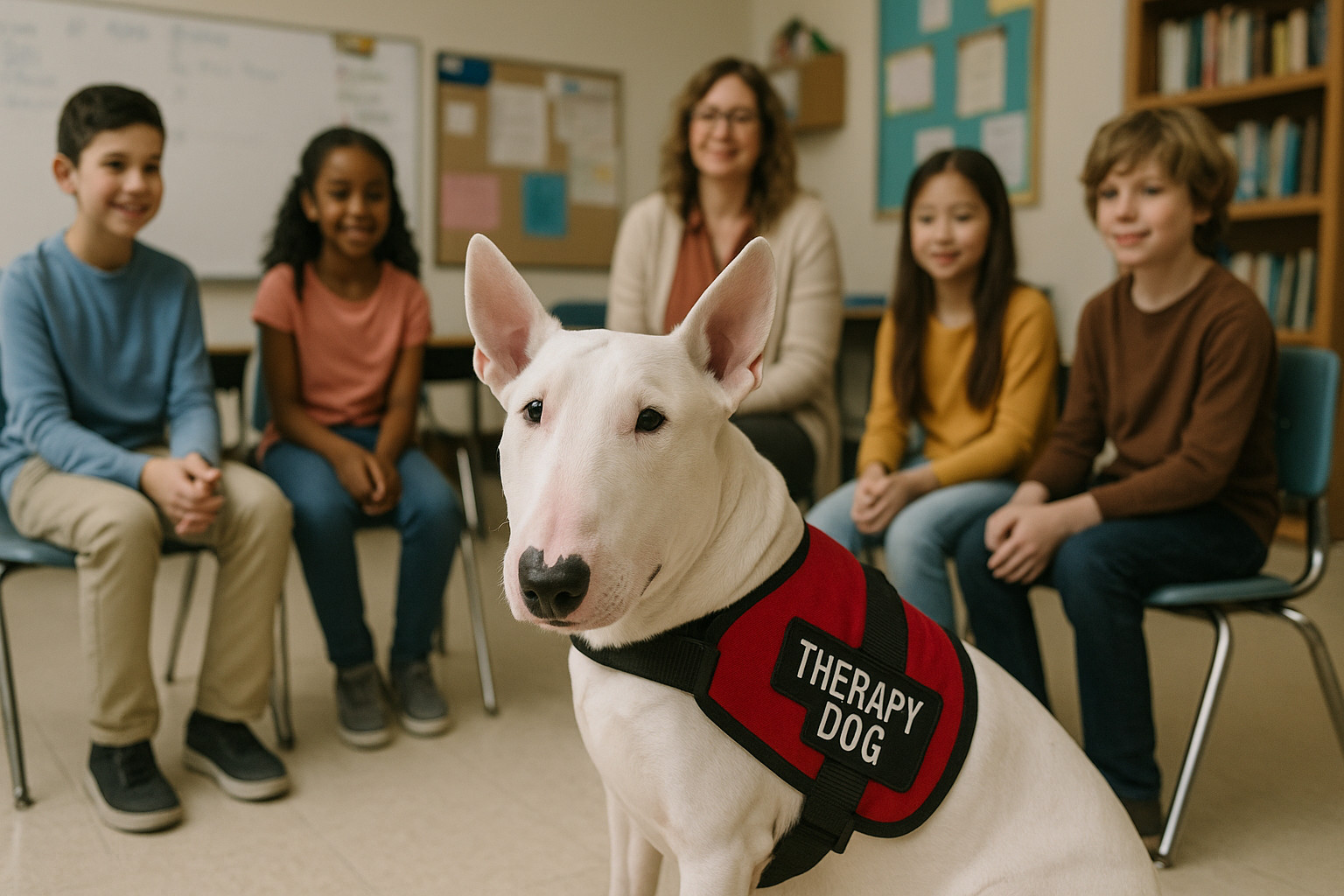

Bull Terrier as a Therapy Dog Overview
The Bull Terrier, known for its distinctive egg-shaped head and robust physique, may not be the first breed one associates with therapy work. Yet, its unique blend of exuberance, loyalty, and intelligence makes it a compelling candidate for animal-assisted therapy roles. Historically bred for tenacity and strength, today’s Bull Terrier exhibits a friendliness and curiosity that, when guided correctly, can thrive in therapeutic settings. Understanding how this breed’s specific traits contribute to its success or challenges in these roles can aid handlers, trainers, and healthcare professionals in leveraging their abilities effectively.
Understanding the Therapy Dog Role
Therapy dogs, unlike service or working dogs, provide comfort and companionship to people in various settings, from hospitals to nursing homes. Their primary role involves interacting with individuals to enhance emotional well-being, alleviate stress, and provide a sense of calm and joy. Therefore, the ideal therapy dog is one with a balanced temperament, marked by empathy, calmness, and adaptability. A dog’s effectiveness in these settings is as much about its training as it is about its natural disposition and emotional intelligence.
Physical Appearance and Energy Level
The Bull Terrier is a medium-sized, muscular dog with a sleek coat and a high-energy disposition. While their physical strength might suggest a more robust role, their playful and affectionate nature offers a softer side perfect for therapy. However, their high energy levels require careful management to ensure they remain composed during therapy sessions. Regular exercise is crucial not only for their physical health but also to maintain a calm demeanor required in therapeutic environments.
- Pros: Physical presence can be comforting; their sleek coat requires minimal grooming.
- Cons: High energy may need careful channeling and supervision.
Personality and Emotional Intelligence
The Bull Terrier is known for its exuberance and zest for life, traits that can brighten any room. Their innate curiosity and drive to be involved make them engaging companions in therapy work. This breed forms strong bonds with humans, demonstrating affectionate behavior and a willingness to please. Their emotional intelligence is evident as they quickly perceive changes in human moods and react appropriately, offering comfort and companionship.
- Pros: Strong human bonding and emotional responsiveness enhance therapeutic interactions.
- Cons: Over-exuberance can sometimes be mistaken for hyperactivity; requires structured environments to thrive.
Environments Where Bull Terrier Excels
Bull Terriers can flourish in environments that appreciate their spirited nature. They are well-suited to settings where interaction with people is the primary focus, such as rehabilitation centers and schools. Their playful antics can engage children and aid in physical therapy exercises, while their reassuring presence can provide comfort in retirement homes and hospices.
- Ideal settings: Direct interaction environments such as schools, rehabilitation centers.
- Less ideal: Highly controlled settings where quiet retention is required, like some library programs.
Common Therapy Settings
Therapy work includes various environments, each with specific requirements. Bull Terriers can adapt to many of these with proper training:
- Hospitals and Clinics: Their positive demeanor can uplift patients’ spirits and provide necessary morale boosts.
- Schools: They can serve as reading companions, who encourage literacy efforts in children.
- Rehabilitation Centers: Their playfulness can be harnessed in different therapy activities.
- Nursing Homes: Loyalty and affection offer much-needed companionship to the elderly.
Interactions with Different Populations
The Bull Terrier’s friendly nature is particularly effective in engaging with different age groups:
- Children: Their playful nature appeals to kids, making them great additions in pediatric therapy settings.
- Adults: Can create positive interactions that relieve stress and provide emotional support.
- Elderly: Their calming presence aids in fighting isolation and loneliness, commonly seen in elderly demographics.
Health and Wellness Factors
Health is a significant consideration when evaluating a Bull Terrier for therapy work. A healthy Bull Terrier can endure longer therapy sessions without fatigue, making regular health check-ups essential.
Lifespan and Common Health Issues
With a lifespan of 10-14 years, Bull Terriers, like all breeds, face certain health challenges:
- Common Issues: Skin allergies, deafness, and knee problems.
- Impact on Therapy Work: Skin issues could limit their contact with sensitive-skinned individuals. Regular health assessments are crucial to catch early signs of problems.
Maintenance and Care Needs
The Bull Terrier requires standard grooming practices as well as regular physical activity to maintain composure in therapy settings. Given their short coat, they are relatively low maintenance concerning grooming; however, regular baths and brushing help minimize shedding issues, ensuring their readiness for interactions in therapy environments.
Training and Certification Readiness
Effective therapy dogs require specific training to ensure they manage varied environments with grace and awareness. Bull Terriers, while intelligent, can be stubborn, which demands a patient and positive approach to training. Consistent socialization from a young age is crucial to preparing them for therapy certification tests, which gauge their ability to interact with different individuals and remain calm under diverse stimuli.
Learning Style and Responsiveness
Bull Terriers learn best in engaging, fun environments where consistent encouragement is prevalent. Trainers must find creative ways to maintain their interest without letting their natural playful behavior turn disruptive. Their strong desire to please can be harnessed to teach them gentle behavior around fragile individuals and how to adapt their energy levels according to the setting.
Handling Social and Emotional Stimuli
Bull Terriers are highly receptive to social and emotional cues, making them effective in therapy sessions involving emotional expression. Their reactions to stimuli need guidance to prevent overreactions, but with the proper training, they can detect subtle emotional states and respond with comforting behaviors.
Strengths, Limitations, and Ideal Roles for Bull Terrier
Strengths:
- High energy levels can invigorate environments.
- Emotional intelligence allows them to form meaningful connections.
Limitations:
- Potential for over-excitement; requires careful environmental management.
- Health issues, if unmonitored, can limit therapy effectiveness.
Ideal Roles:
- Engaging with children and active adults.
- Participation in therapeutic physical activities where energy can be positively directed.
Final Thoughts
In essence, the Bull Terrier’s potential as a therapy dog lies in its ability to fill a room with energy and warmth while forming profound connections with those around them. Their natural curiosity and zest for life, partnered with well-directed training, allow them to be effective conduits of joy and healing in diverse therapy settings.
Key Takeaways for the Bull Terrier as a Therapy Dog
- Best suited for: Environments needing energy and engagement, like schools and rehabilitation centers.
- Not ideal for: Settings demanding constant calm, such as book libraries.
- Temperament highlights: Affectionate, intelligent, and high-spirited, with strong emotional connections.
- Care and health notes: Regular exercise and minimal grooming required; monitor for common health issues.
- Therapy environments where they shine: Schools, nursing homes, rehabilitation centers, and other dynamic settings requiring active engagement.
Get Your Documents
Example State Cards