Great Pyrenees as a Therapy Dog
Get Your Documents
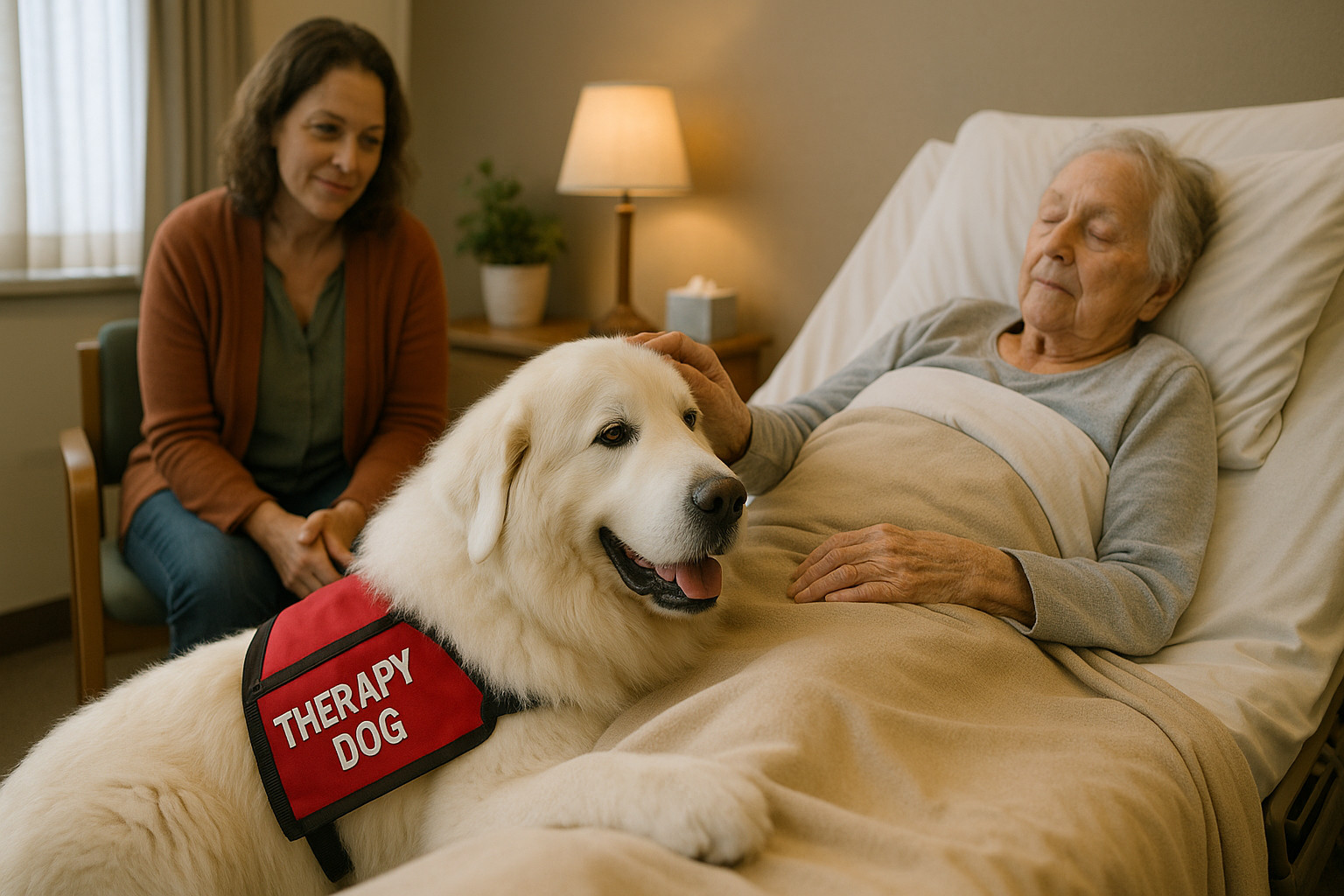

Great Pyrenees as a Therapy Dog Overview
The Great Pyrenees is a breed known for its majestic appearance, gentle demeanor, and unwavering loyalty, making it a remarkable candidate for therapy work. As therapy dogs, Great Pyrenees can leave a lasting impact on individuals in need of emotional comfort and support. Their deep empathetic nature and ability to remain calm in a variety of settings ensure they excel in creating a peaceful environment for those they interact with.
Understanding the Therapy Dog Role
Therapy dogs are trained to provide comfort, affection, and emotional support to people in numerous settings, including hospitals, schools, and nursing homes. Contrary to service dogs with specific task-driven roles, therapy dogs primarily enhance emotional well-being through presence and interaction.
Great Pyrenees possess an inherent ability to connect with humans, making them suitable for therapy roles. They provide companionship in healing journeys, especially beneficial for individuals experiencing stress, anxiety, or depression. These interactions often include:
- Relieving tension and lowering blood pressure through their calm presence
- Offering non-judgmental companionship that encourages self-expression
- Acting as a comforting and grounding presence in clinical environments
Physical Appearance and Energy Level
The Great Pyrenees is a large and visually striking breed, characterized by its thick, white double coat and gentle expression. Despite their considerable size, these dogs have a demeanor often described as serene and composed.
Their physical characteristics contribute to their efficacy as therapy dogs, as they possess an inviting, reassuring presence:
- Majestic Appearance: Their size and regal stature command attention and respect, often making them a comforting focal point.
- Energy Level: Known for their low to moderate energy levels, Great Pyrenees maintain a calm demeanor, which works well in environments where a peaceful atmosphere is desired.
These traits allow Great Pyrenees to engage effectively in therapy sessions without overwhelming the individuals they support.
Personality and Emotional Intelligence
The personality of the Great Pyrenees is marked by loyalty, patience, and an innate sense of protectiveness. They exhibit high emotional intelligence, which allows them to perceive and respond to human emotions effectively:
- Empathy: Great Pyrenees are highly attuned to human emotions, often sensing distress and offering solace in a way that feels intuitive and spontaneous.
- Calmness: Their docile nature makes them excellent at maintaining a stable and soothing environment.
- Adaptability: Although they are naturally wary of strangers, with proper socialization, they adapt to new people and situations, which is crucial in a therapy dog role.
The breed’s keen intuition and ability to mirror human emotions make them significant assets in emotionally charged settings.
Environments Where Great Pyrenees Excels
Therapy dogs operate in various environments, each with unique demands. The Great Pyrenees pour their calming energy and empathetic presence into settings that allow them to engage meaningfully with individuals or groups. They perform most effectively in places where:
- Quiet, Controlled Environments: Their large size and serene nature suit calm and relatively quiet settings.
- Spaces Requiring a Gentle Touch: They excel in calming or non-threatening spaces, enhancing therapeutic outcomes through their soothing presence.
The following are examples of environments where Great Pyrenees naturally excel as therapy dogs:
#### Common Therapy Settings
- Hospitals: In a clinical setting, their presence provides mental relief to patients and family members, reducing stress and anxiety associated with medical procedures.
- Nursing Homes: Older adults often find comfort in interacting with dogs, and the Great Pyrenees’ steady temperament makes them ideal for providing companionship to the elderly.
- Rehabilitation Centers: As a source of motivation and emotional support, they aid individuals in psychosocial rehabilitation, boosting morale and aiding progress.
- Schools: Their gentle, non-intrusive nature helps comfort children in educational settings, particularly those with anxiety or special needs.
Interactions with Different Populations
The breed’s capacity to connect with diverse populations is a highlight of their therapy capabilities. Great Pyrenees excel in interactions with individuals across the age spectrum and various emotional and physical needs:
- Children: Their patient and protective instincts help alleviate anxiety and promote a sense of safety.
- Adults with Mental Health Challenges: Through non-verbal communication, they offer comfort and reduce feelings of isolation and sadness.
- Elderly Individuals: Their tranquil nature helps soothe and uplift older adults, providing companionship that reduces feelings of loneliness.
By tailoring their behavior to suit the emotional and physical capacities of different individuals, Great Pyrenees prove versatile in their role as therapy dogs.
Health and Wellness Factors
Understanding the breed’s health profile is crucial for maintaining their well-being, which directly impacts their effectiveness as therapy dogs.
- Lifespan: Typically 10–12 years, their longevity allows for extended therapeutic partnerships.
- Common Health Issues: Being prone to health issues such as hip dysplasia and bloat, routine veterinary check-ups and proper diet management are essential.
- Grooming Needs: Regular grooming is necessary to manage their dense double coat and ensure they remain hygienic and comfortable in therapy settings.
Proper health and wellness care enhances their ability to perform consistently and comfortably in therapy roles.
Training and Certification Readiness
Great Pyrenees require structured training to fine-tune their natural capabilities for therapy work. Their trainability can be influenced by:
- Learning Style: They possess an independent streak; therefore, training should be consistent yet patient, emphasizing positive reinforcement.
- Responsiveness: Early socialization is vital to hone their responsiveness and adaptability to various stimuli and environments.
Certification requires these dogs to meet behavioral standards, showcasing their suitability for therapy services through evaluative processes.
Handling Social and Emotional Stimuli
A prominent trait of the Great Pyrenees is its ability to process and respond to social and emotional stimuli effectively:
- Sensitivity to Emotional Cues: They demonstrate acute sensitivity to the emotional states of humans, often adjusting their behavior to provide comfort.
- Socialization: Proper and gradual exposure to diverse environments ensures they remain composed and responsive, which is crucial for therapy settings.
Daily mental stimulation and understanding of human emotions allow them to interact meaningfully within varied contexts.
Strengths, Limitations, and Ideal Roles for Great Pyrenees
The Great Pyrenees present notable strengths and particular limitations in their role as therapy dogs:
- Strengths: Include their calming presence, empathy, and adaptability, which make them excellent companions in therapeutic settings.
- Limitations: Their size can be intimidating to some individuals, and they may exhibit slight aloofness, requiring thorough socialization.
- Ideal Roles: They excel in settings requiring a gentle, steady presence, such as in elder care or smaller group therapy sessions.
Final Thoughts
The Great Pyrenees is a breed exceptionally suited for therapy work, offering comfort and companionship through their empathy and gentle nature. Their physical and emotional traits, coupled with a serene presence, make them a valuable asset in many therapeutic environments. While their size may present challenges, with proper training and socialization, the Great Pyrenees can enrich the therapeutic experience for countless individuals.
Key Takeaways for the Great Pyrenees as a Therapy Dog
- Best suited for: Hospitals, nursing homes, rehabilitation centers, and schools where a calming presence is needed.
- Not ideal for: Highly active or bustling environments that require a higher energy presence.
- Temperament highlights: Empathetic, calm, and patient, with a strong ability to sense and react to emotions.
- Care and health notes: Regular grooming and consistent health monitoring are essential to maintain their welfare and effectiveness.
- Therapy environments where they shine: Quiet, structured settings that allow for calm interactions and meaningful connections.
Get Your Documents
Example State Cards