Pug as a Therapy Dog
Get Your Documents

Pug as a Therapy Dog Overview
The Pug is a charming and affectionate companion breed known for its loving nature and ability to forge strong bonds with humans. As a therapy dog, the Pug’s inherent temperament, unique physical attributes, and emotional intelligence make it a remarkable candidate. This article explores the various aspects of the Pug as a therapy dog, highlighting its capabilities, limitations, training needs, and ideal therapy settings.
Understanding the Therapy Dog Role
Therapy dogs play a vital role in providing emotional support, promoting healing, and enhancing the quality of life for individuals in various settings. These dogs are assessed not just on their ability to interact with people but on their capacity to offer comfort, mitigate stress, and improve mood.
Therapy dogs are utilized in diverse environments, including hospitals, nursing homes, schools, and rehabilitation centers, where human-animal interactions can have therapeutic benefits. While they don’t have the same rights of access as service dogs, their presence can immensely benefit those they interact with.
Physical Appearance and Energy Level
The Pug is a small, compact dog breed weighing between 14 and 18 pounds, with a distinctive wrinkled face and curled tail. Their small size allows for easy maneuverability in close quarters such as hospital rooms or classrooms, making them ideal for therapy-related tasks in confined settings.
Despite their compact size, Pugs have a moderate energy level and can adapt well to both active and relaxed environments. Their energy level, while not overly exuberant, is sufficient to engage with people effectively without causing unnecessary disturbance, making them perfect for settings that require calm and gentle interactions.
Personality and Emotional Intelligence
Pugs possess a naturally affectionate and stable temperament, making them excellent candidates for therapy work. Their charismatic personality and inherent desire to be close to people help establish immediate rapport, crucial for therapy settings where trust and comfort are paramount.
- Empathy and Understanding: Pugs display a significant level of empathy, often sensing emotional cues and responding appropriately. Their ability to remain calm and approachable helps them connect deeply with people needing comfort.
- Adaptability: Pugs are adaptable and can adjust their behavior based on the environment and the emotional needs of those they interact with. Their adaptability enhances their effectiveness across varying therapy situations.
Environments Where Pug Excels
Pugs are particularly suited to environments that value interaction and engagement without demanding high physical exertion or hyperactivity. Their small size and manageable energy levels make them ideal for:
- Hospitals and Healthcare Facilities: Their ability to provide quiet companionship can alleviate anxiety and provide comfort to patients.
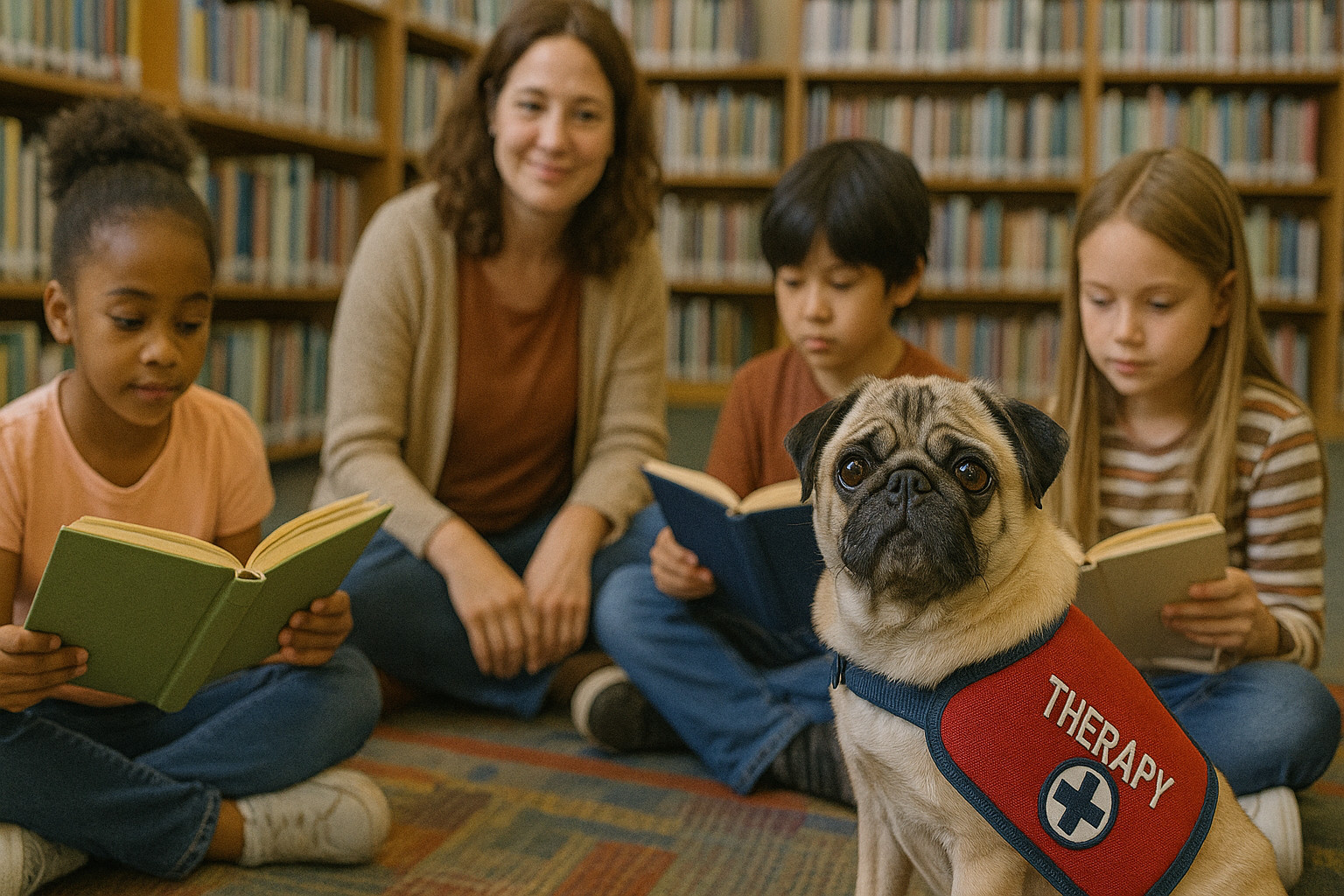
- Educational Settings: Pugs can engage with children in schools or libraries, promoting emotional support or acting as reading companions.
- Nursing Homes and Senior Centers: Elderly individuals can benefit from the affectionate companionship of a Pug, who is reliable and gentle.
Common Therapy Settings
In therapy settings, the Pug thrives where gentle interaction is key. Their gentle nature allows them to work well in environments such as:
- Physical Rehabilitation Centers: Where their presence can motivate patients during recovery exercises.
- Mental Health Facilities: Offering solace and non-judgmental companionship to individuals struggling with various mental health issues.
- Youth Programs: Serving as gentle motivators or calming presences to youths participating in developmental activities.
Interactions with Different Populations
Pugs demonstrate a unique ability to interact positively across age groups and populations due to their gentle demeanor and affection:
- With Children: Their playful yet calm nature creates a soothing presence for children, fostering a supportive environment for learning or healing.
- With the Elderly: Pugs provide unconditional companionship, which can be profoundly comforting for seniors experiencing loneliness or cognitive decline.
- With Individuals with Disabilities: Their empathetic demeanor allows for meaningful connections, aiding emotional and therapeutic outcomes.
Health and Wellness Factors
The health and wellness of therapy dogs are paramount to ensure safety and efficacy in their roles. Pugs are prone to certain health issues that should be considered in the context of therapy work.
#### Lifespan and Common Health Issues
Pugs generally live between 12 to 15 years. Common health issues include:
- Brachycephalic Syndrome: Due to their short muzzles, Pugs may experience breathing difficulties, especially in stressful environments, which can affect their therapy performance.
- Obesity: Pugs are prone to weight gain, requiring a balanced diet and regular exercise to maintain optimal health and performance as a therapy dog.
- Eye Problems: Their prominent eyes are susceptible to injuries and infections, necessitating regular veterinary check-ups.
Maintenance and Care Needs
To maintain a Pug’s readiness and effectiveness as a therapy dog, consistent grooming and health management are essential. Their grooming routine includes:
- Regular Brushing: To control shedding and maintain a healthy coat.
- Facial Wrinkle Cleaning: Routine cleaning of facial wrinkles prevents infections and maintains their distinctive appearance.
- Eye and Ear Care: Regular checks and cleaning help prevent irritation and infections.
Training and Certification Readiness
The trainability of a Pug is enhanced by its intelligence, although patience is often required given their independent streak.
#### Learning Style and Responsiveness
Pugs respond well to positive reinforcement and consistent, gentle training methods. They exhibit:
- Good Social Skills: These traits make them responsive to training focused on behavior that reinforces their natural ability to comfort and engage.
- Adaptation to Routine: With a structured routine, Pugs can excel in therapy duties, responding positively to clearly defined tasks.
Handling Social and Emotional Stimuli
Pugs demonstrate an ability to handle social stimuli by leveraging their calm and stable demeanor. They are known to be:
- Unfazed by New Faces: Allowing them to quickly adapt to new people or environments without stress.
- Emotionally Resilient: Helping them maintain composure even in volatile or highly emotional therapy settings.
Strengths, Limitations, and Ideal Roles for Pug
Strengths:
- Innate ability to connect emotionally with varied populations.
- Calm demeanor suitable for sensitive environments.
- Small size lends to versatility and ease of mobility across settings.
Limitations:
- Potential breathing difficulties in stressful situations.
- Prone to health issues that require close management.
- Independently minded, requiring patient and persistent training.
Ideal Roles:
- Making frequent visits to children’s hospitals.
- Providing companionship in senior living communities.
- Supporting emotional learning and interaction in educational settings.
Final Thoughts
The Pug’s gentle and affectionate nature makes it a suitable candidate for therapy work, especially in environments that thrive on warmth and empathy. While there are health considerations to manage, their temperament typically yields positive results, earning them a special place in various therapeutic fields.
Key Takeaways for the Pug as a Therapy Dog
- Best suited for: Healthcare facilities, educational settings, elderly care.
- Not ideal for: High-stress or physically demanding therapy roles.
- Temperament highlights: Affectionate, calm, adaptable, empathetic.
- Care and health notes: Prone to obesity, breathing issues, and eye conditions; require consistent health management.
- Therapy environments where they shine: Hospitals, schools, nursing homes, and rehabilitation centers.
Get Your Documents
Example State Cards